Rick Wolff
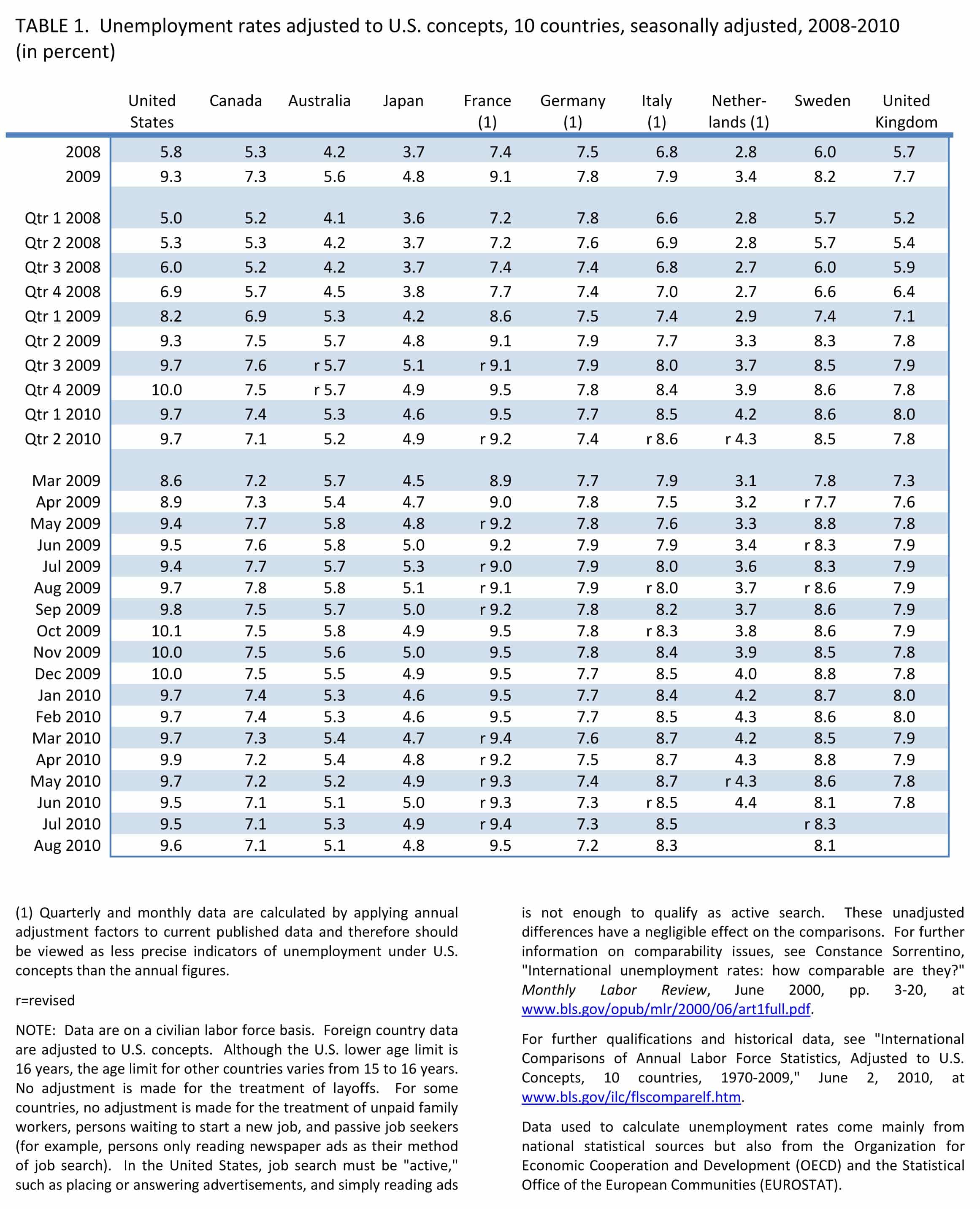
US workers suffered a major rise in unemployment from its level in 2008 (5.8 %) to its level in the second quarter of 2010 (9.7 %). By comparison, French unemployment rose from 7.4 % in 2008 to 9.2 % in the second quarter of 2010. These data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) show clearly that unemployment rose further and faster in the US than in France across this crisis's first three years.
What differentiates French labor activism from US labor passivism are decades in which US labor unions and the US left declined in size, militancy, and social influence far further and faster than their French counterparts. In France the electorate and mass public opinion are now swinging left against the austerity policies of the Sarkozy government in solidarity with the leadership shown by labor and the left. French public opinion polls show that two-thirds of French public opinion either supports or is sympathetic with the repeated huge labor strikes and demonstrations against austerity. Such poll results in favor of these massive actions are not only extraordinarily high but also have been stable for months at that height. In contrast, within the different US conjuncture, the Democrats fear a major electoral loss in November 2010, to an extremely conservative, pro-austerity Republican party.
One key lesson of this crisis's different evolution in the US and France is this: the basic economic welfare of the working majority inside a modern industrial capitalism depends on maintaining a strong, militant trade union movement and a strong anti-capitalist movement and tradition. In France, labor and the left always included socially significant groups and movements, theoretical and practical, who were critical of capitalism and committed to basic social change beyond capitalism. That organized radicalism kept alive the notion of a real alternative to the present system. It also sustained many complex connections among militants. Those connections are now being effectively mobilized to forge an historic resistance inside capitalism to its costly crises and the ruling class's response to them. Moreover, because of its anti-capitalist components, that resistance may mature into a social movement for basic social change.




















Sem comentários:
Enviar um comentário